Sometimes, customer journeys may seem simple and straightforward, however, your customers go through a variety of stages and experiences before buying your product and actually becoming your customers. Behind a chunk of customers, there is always a group of people who thought of buying a product or service but actually did not convert.
Researches suggest that around 70% of online shoppers abandon their carts without actually making a purchase due to several reasons for cart abandonment. So it is imperative to understand customer experiences throughout the customer journey to identify the gaps in between and eliminate them to provide better customer experiences throughout the customer journey and encourage more potential customers to convert. Here comes the need for customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping is a great way to gain insights into every touchpoint and experience that your customers go through. In this article, we will learn with examples, how customer journey mapping can be done in various industries. Let’s start with exploring what customer journey mapping exactly is and how it is important for your business.
TL;DR
- Customer journey mapping is the process of visually representing customer journey touchpoints which helps businesses understand and optimize the customer experience at various touchpoints throughout the customer journey.
- Customer journey mapping is important for understanding customers' pain points, increasing customer retention, tracking staff performance, planning marketing strategies to encourage more conversions, and delivering better customer experiences.
- Examples across various industries illustrate how customer journey mapping can be applied to improve experiences, from retail to healthcare, hotels, education, restaurants, and airlines.
- Integrating customer journey mapping with the customer lifecycle allows businesses to tailor strategies to meet evolving customer needs at each stage.
- Zonka Feedback, a customer feedback software, can help gather feedback at every touchpoint, enabling businesses to improve customer experience and drive growth effectively. It also offers a free trial for 14 days.
Fuel Business Growth with Customer Feedback 🔥
Collect real-time, in-moment feedback at all touchpoints in customer journey and leverage feedback insights to transform customer experience.

What is Customer Journey Mapping?
Customer journey mapping is the process of visually representing customers’ entire journey with a business or a brand. It involves mapping out every touchpoint at which customers interact and go through, across various channels, from the initial awareness stage to post-purchase support.
The main objectives of this visual representation are to identify key moments a customer or potential customer goes through, customers' pain points that affect customer experience, and opportunities for improvement, and to build long-term customer loyalty.
By creating a detailed depiction of the customers’ experiences, you can gain insights into their needs, preferences, and behaviors, which enables you to create your business strategies accordingly and enhance overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Why is Customer Journey mapping Important?
Customer journey mapping is an essential practice for businesses looking to gain a deeper understanding of their customers and improve the overall customer satisfaction. Here's why it is important to create a customer journey map:
-
Understanding Customers' Pain Points: By meticulously mapping out the customer journey, you can pinpoint areas where customers encounter challenges or frustrations. This insight allows you to address customer pain points proactively, leading to smoother interactions and increased customer satisfaction.
-
Increasing Customer Retention: Identifying and resolving pain points along the customer journey can significantly enhance retention rates. When customers have positive experiences at every touchpoint, they are more likely to remain loyal to the brand and continue purchasing your products or services.
-
Tracking Staff Performance: Customer journey mapping provides valuable insights into how employees like sales reps and customer service reps or support agents interact with customers at each stage of the journey. By monitoring staff performance, you can identify areas where additional training or support may be needed to ensure consistent and high-quality customer service.
-
Planning Better Marketing Strategies: By understanding the customer journey, you can make your marketing strategies better to meet the needs and preferences of your target audience. This allows you to deliver more relevant and personalized marketing, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates.
-
Delivering Better Customer Experiences: Ultimately, customer journey mapping is about delivering exceptional experiences that exceed customer expectations. By identifying opportunities to streamline processes, eliminate friction points, and enhance interactions, businesses can create memorable experiences that foster loyalty and advocacy.
Let’s learn about customer journey mapping for various Industries.
Customer Journey Maps Examples for Various Industries
There are various stages of the customer journey for different industries. Creating a customer journey map helps you focus on every touchpoint of the journey and helps to find out where customers are facing any issues.
Here are the different touchpoints of the customer journey in various industries:
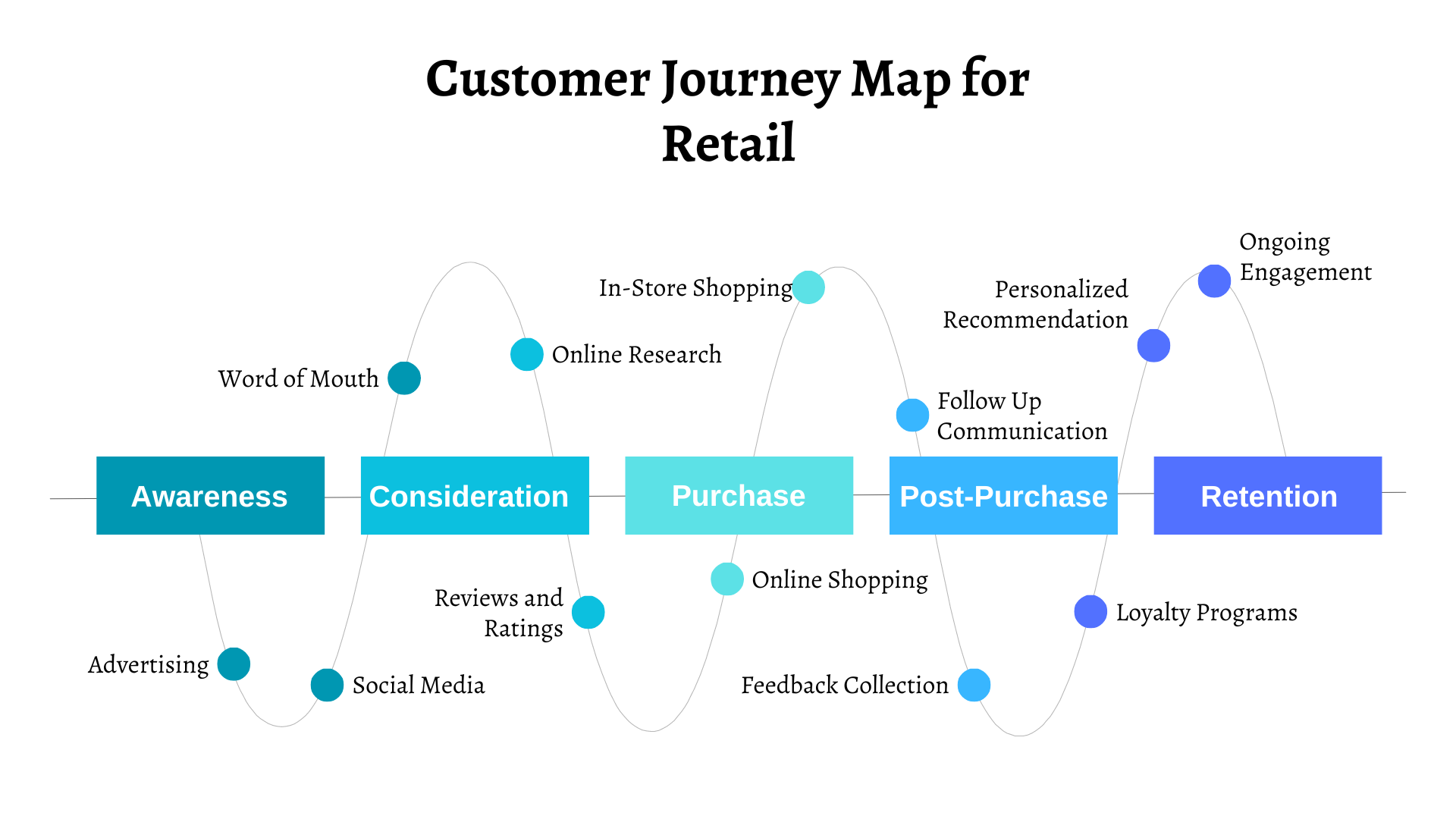
Customer Journey Map for Retail
In the retail industry, understanding the buyer's journey from initial awareness to post-purchase support is crucial for building lasting relationships and driving sales.
Stage 1. Awareness
Customers become aware of retail brands through advertising, social media, or word-of-mouth through the following channels or touchpoints.
- Advertising: Customers come across the retail brand through various advertising channels such as TV commercials, billboards, online ads, and print media.
- Social Media: Customers discover the retail brand through posts, ads, and sponsored content on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
- Word-of-mouth: Customers learn about the retail brand through recommendations from friends, family, or colleagues who have had positive experiences.
Stage 2. Consideration
Customers research products online, read reviews, and compare prices.
- Online Research: Customers conduct online research to explore different products, brands, and options available in the market. They visit the retailer's website, read product descriptions, and compare features and prices. As customers explore their options during the consideration stage, targeted advertising can significantly influence their perceptions and decisions. Agencies specializing in marketing and PPC audit, provide strategic ad placements that help capture the attention of potential buyers at this crucial point, enhancing the likelihood of conversion.
- Reviews and Ratings: Customers read reviews and ratings on the retailer's website, third-party review platforms, and social media to gather insights from other shoppers' experiences.
- Price Comparison: Customers compare prices across different retailers, both online and offline, to find the best deals and value for their money.
Stage 3. Purchase
Customers make purchases either online or in-store, influenced by factors such as convenience, price, and product availability.
- Online Shopping: Customers make purchases through the retailer's website or mobile app, adding items to their cart, selecting shipping options, and completing the checkout process.
- In-Store Shopping: Customers visit physical retail locations, browse products on shelves or racks, interact with sales associates, and proceed to checkout counters to make purchases.
- Factors Influencing Purchase: Customers' purchase decisions are influenced by factors such as convenience, price competitiveness, product quality, availability, and brand reputation.
Stage 4. Post-Purchase
Follow-up communication, feedback collection, and opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
- Follow-up Communication: Retailers send follow-up communication to customers after their purchase, such as order confirmation emails, shipping notifications, and delivery updates.
- Feedback Collection: Retailers solicit feedback from customers through surveys, emails, or in-store feedback terminals to gather insights on their shopping experience and satisfaction levels.
- Opportunities for Upselling or Cross-selling: Retailers present opportunities for customers to purchase complementary products, accessories, or upgrades through targeted marketing messages, recommendations, and promotions.
Stage 5. Retention
Loyalty programs, personalized recommendations, and ongoing engagement to encourage repeat purchases.
- Loyalty Programs: Retailers offer loyalty programs that reward customers for repeat purchases, referrals, and engagement with exclusive discounts, rewards points, or VIP perks.
- Personalized Recommendations: Retailers use customer data and purchase history to deliver personalized product recommendations, offers, and promotions tailored to individual preferences and behaviors.
- Ongoing Engagement: Retailers engage with customers through email newsletters, social media updates, special events, and promotions to maintain ongoing relationships and encourage repeat purchases.
Example: Nike
Nike employs customer journey mapping to enhance the shopping experience both online and in-store. They track customer interactions across various touchpoints, including their website, mobile app, social media, and physical retail stores.
Successful Strategy: Nike's personalized product recommendations based on past purchases and browsing history are a successful strategy. By leveraging data analytics, they deliver targeted marketing messages and offers, creating a seamless shopping experience that resonates with each customer's preferences and needs.
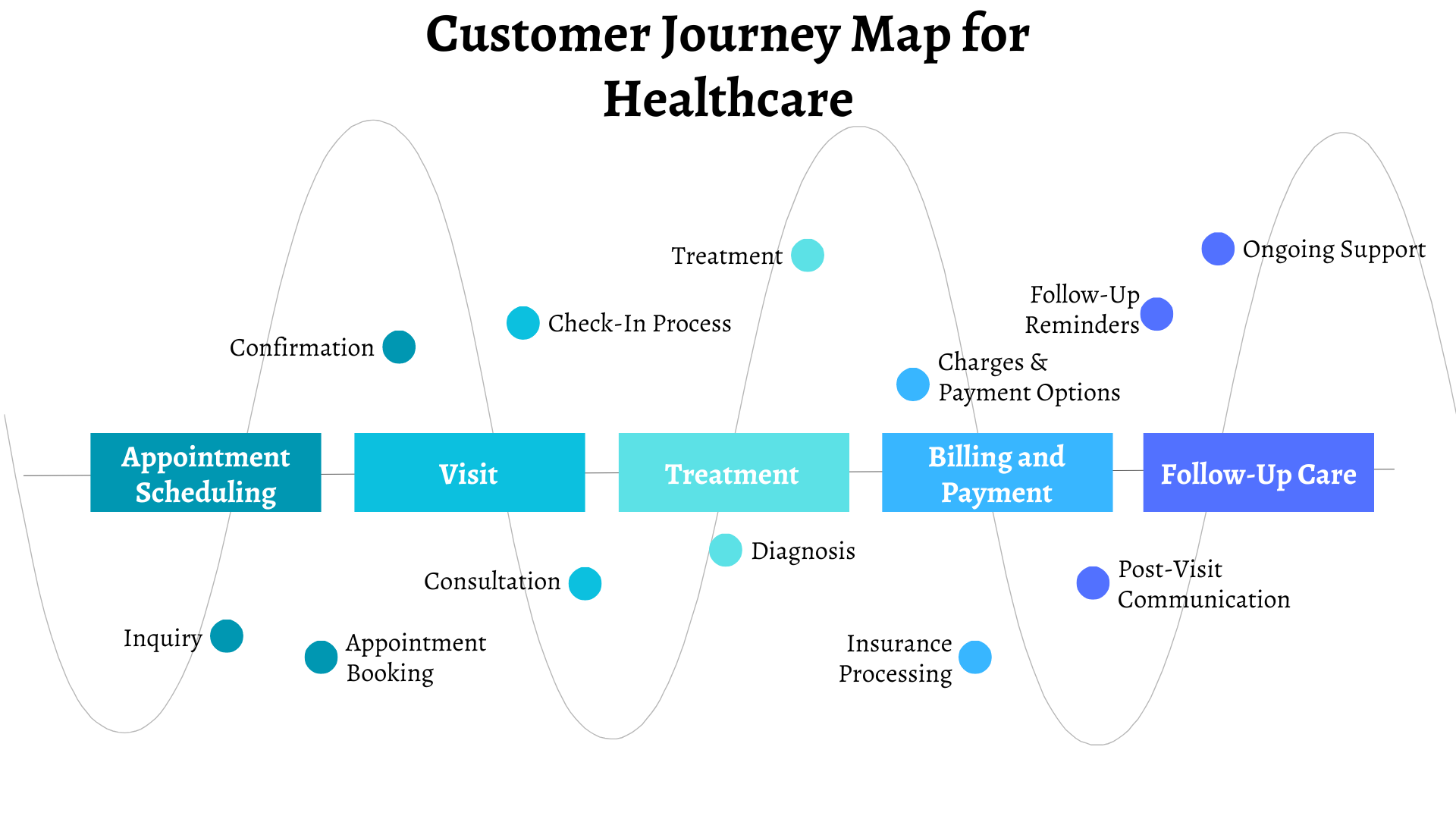
Customer Journey Map for Healthcare
Navigating the healthcare journey involves various touchpoints that ensure patients receive quality care and support throughout their treatment.
Stage 1. Appointment Scheduling
Patients contact healthcare providers to schedule appointments, either online or by phone.
- Inquiry: Patients initiate contact with healthcare providers to schedule appointments, seeking medical consultations, examinations, or treatments for specific health concerns or conditions.
- Appointment Booking: Patients communicate with scheduling staff or use an appointment scheduling app to secure appointment slots, providing personal information, preferred dates/times, and reasons for seeking medical attention.
- Confirmation: Patients receive confirmation of their scheduled appointments via email, SMS, or phone call, along with instructions regarding preparation, documentation, or additional requirements.
Stage 2. Visit
Arrival at healthcare facilities, check-in process, and consultation with healthcare professionals.
- Arrival: Patients arrive at healthcare facilities at scheduled appointment times, presenting themselves to reception or check-in areas for registration, verification of identity, and initial assessment.
- Check-in Process: Patients complete administrative tasks, such as filling out forms, updating medical histories, and verifying insurance coverage, to facilitate smooth admission into the healthcare system.
- Consultation: Patients meet with healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, or specialists, for comprehensive evaluations, medical examinations, and discussions regarding symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment options.
Stage 3. Treatment
Diagnosis, treatment plans, medication prescriptions, and follow-up instructions.
- Diagnosis: Patients undergo diagnostic procedures, tests, or evaluations to identify underlying health issues, illnesses, or medical conditions, utilizing advanced medical technologies and expertise to inform treatment decisions.
- Treatment Plans: Patients receive personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs, comprising medication prescriptions, surgical interventions, therapy sessions, lifestyle modifications, or referrals to other healthcare providers or specialists.
- Medication Prescriptions: Patients are prescribed medications based on their diagnoses and treatment plans, with healthcare professionals providing detailed instructions on dosage, frequency, potential side effects, and precautions to ensure safe and effective medication management.
- Follow-up Instructions: Patients receive guidance on post-treatment care, recovery protocols, self-monitoring techniques, and follow-up appointments to track progress, address concerns, and adjust treatment strategies as necessary.
Stage 4. Billing and Payment
Clear explanation of charges, insurance processing, and payment options.
- Explanation of Charges: Patients are provided with transparent explanations of healthcare charges, fees, and expenses associated with services rendered, including consultations, tests, procedures, medications, and hospital accommodations.
- Insurance Processing: Patients navigate insurance-related processes, such as verifying coverage, submitting claims, coordinating benefits, and resolving disputes or discrepancies with insurance providers to facilitate timely and accurate reimbursement.
- Payment Options: Patients have access to various payment options, including cash, credit/debit cards, insurance co-payments, installment plans, or financial assistance programs, to settle outstanding balances and manage healthcare expenses effectively.
Stage 5. Follow-up Care
Post-visit communication, reminders for follow-up appointments, and ongoing support.
- Post-Visit Communication: Patients receive post-visit communication from healthcare providers, such as follow-up calls, emails, or messages, to assess recovery progress, address treatment outcomes, and provide additional medical advice or support as needed.
- Reminders for Follow-up Appointments: Patients receive reminders for scheduled follow-up appointments, screenings, or procedures, helping them stay on track with their healthcare regimen and ensuring continuity of care.
- Ongoing Support: Patients benefit from ongoing support services, resources, or programs offered by healthcare providers, including educational materials, support groups, telemedicine consultations, or referrals to community resources, to enhance health outcomes and overall well-being.
Example: Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic, a renowned healthcare provider, utilizes customer journey mapping to improve patient experiences at every stage of their healthcare journey. They focus on understanding patient needs, preferences, and pain points to deliver exceptional care.
Successful Strategy: One successful strategy employed by Cleveland Clinic is their patient portal, allowing patients to schedule appointments, access medical records, and communicate with healthcare providers online. This digital platform enhances convenience and transparency, empowering patients to take control of their healthcare journey.
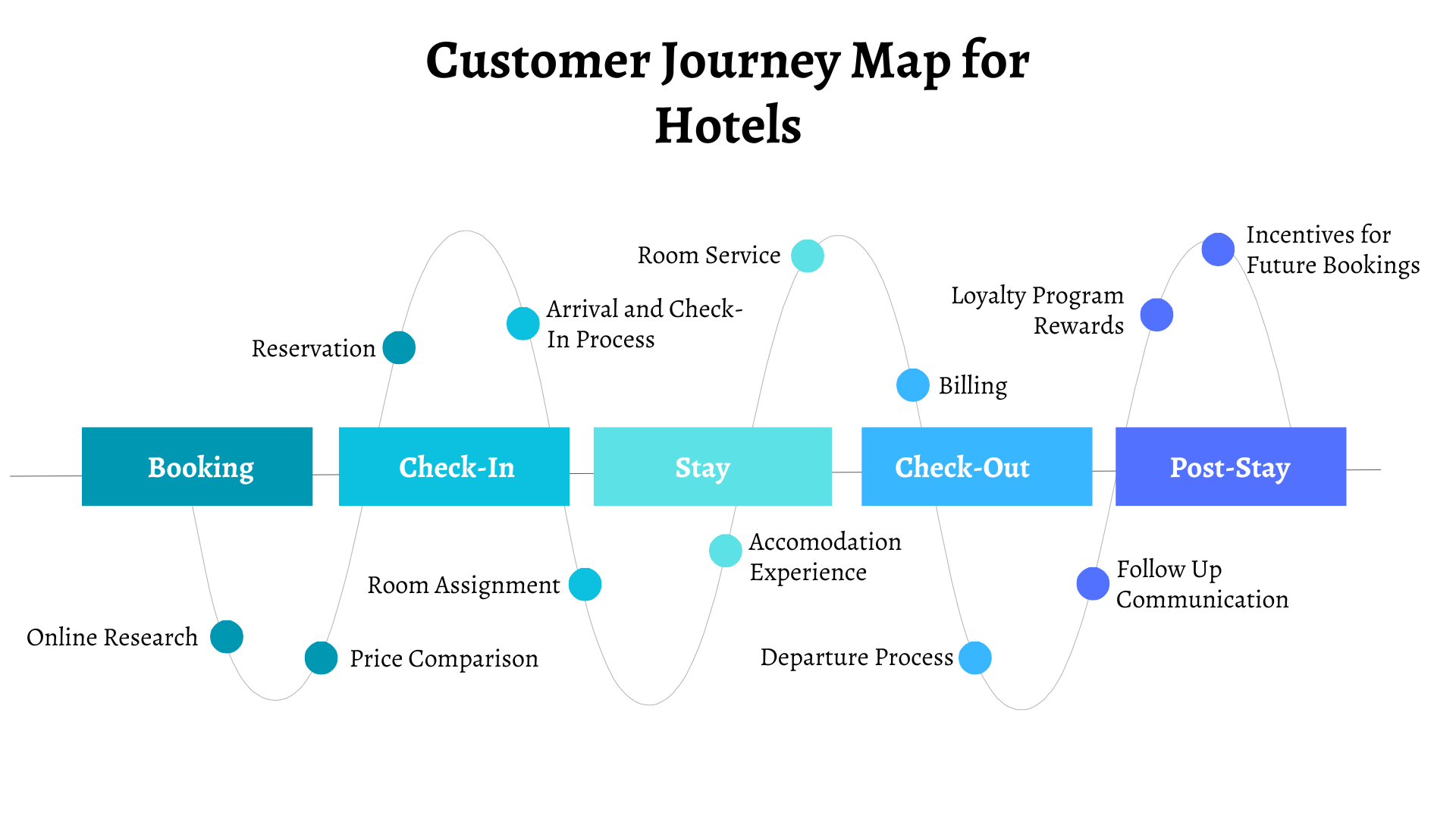
Customer Journey Map for Hotels
The hotel industry focuses on creating memorable experiences for guests by optimizing touchpoints throughout their stay, from booking to departure.
Stage 1. Booking
Guests research hotels online, compare prices, and make reservations.
- Online Research: Guests research hotels online through search engines, travel websites, and booking platforms to explore options, read reviews, and compare prices.
- Price Comparison: Guests compare prices, room availability, and amenities offered by different hotels to find the best value for their stay.
- Reservation: Guests make reservations online through hotel websites or booking platforms by selecting dates, room types, and any special requests.
Stage 2. Check-in
Arrival at the hotel, check-in process, and room assignment.
- Arrival: Guests arrive at the hotel and proceed to the check-in counter or reception area to begin the check-in process.
- Check-in Process: Guests provide identification, payment details, and any special requests to hotel staff, who verify reservations, assign rooms, and provide room keys or access cards.
- Room Assignment: Hotel staff assign rooms based on guest preferences, room availability, and any special requests made during the reservation process.
Stage 3. Stay
Accommodation experience, room service, amenities, and interactions with staff.
- Accommodation Experience: Guests experience their stay, including room comfort, cleanliness, and functionality, as well as access to amenities such as Wi-Fi, TV, minibar, and toiletries.
- Room Service: Guests may request room service for meals, beverages, housekeeping, or maintenance services, which are delivered to their room by hotel staff.
- Amenities: Guests utilize hotel amenities such as swimming pools, fitness centers, spa facilities, business centers, and recreational activities during their stay.
- Interactions with Staff: Guests interact with hotel staff, including front desk agents, concierge, housekeeping, and restaurant/bar staff, for assistance, information, and personalized service throughout their stay.
Stage 4. Check-out
Billing, feedback collection, and departure process.
- Billing: Guests settle their bills at the check-out counter, where hotel staff provide an itemized receipt of charges, including room rate, taxes, and any additional services or amenities used during the stay.
- Feedback Collection: Hotel staff may request feedback from guests regarding their stay, inviting them to share their experiences, suggestions, or concerns to improve service quality.
- Departure Process: Guests return room keys or access cards, retrieve any belongings stored with the hotel, and complete the check-out process before leaving the property.
Stage 5. Post-Stay
Follow-up communication, loyalty program rewards, and incentives for future bookings.
- Follow-up Communication: Hotels may send follow-up communication to guests after their stay, including thank-you emails, surveys, or special offers for future bookings.
- Loyalty Program Rewards: Guests enrolled in hotel loyalty programs may receive rewards points, discounts, or exclusive offers based on their stay history and membership status.
- Incentives for Future Bookings: Hotels may offer incentives such as discounts, upgrades, or complimentary services to encourage guests to book future stays with them.
Example: Marriott International
Marriott International employs customer journey mapping to optimize the guest experience across its portfolio of hotels and resorts worldwide. They analyze guest feedback, preferences, and behaviors to tailor services and amenities to meet evolving customer expectations.
Successful Strategy: Marriott's mobile check-in and keyless entry feature is a successful strategy. Guests can bypass the front desk and use their smartphones to check in and access their rooms, streamlining the arrival process and enhancing convenience for travellers.
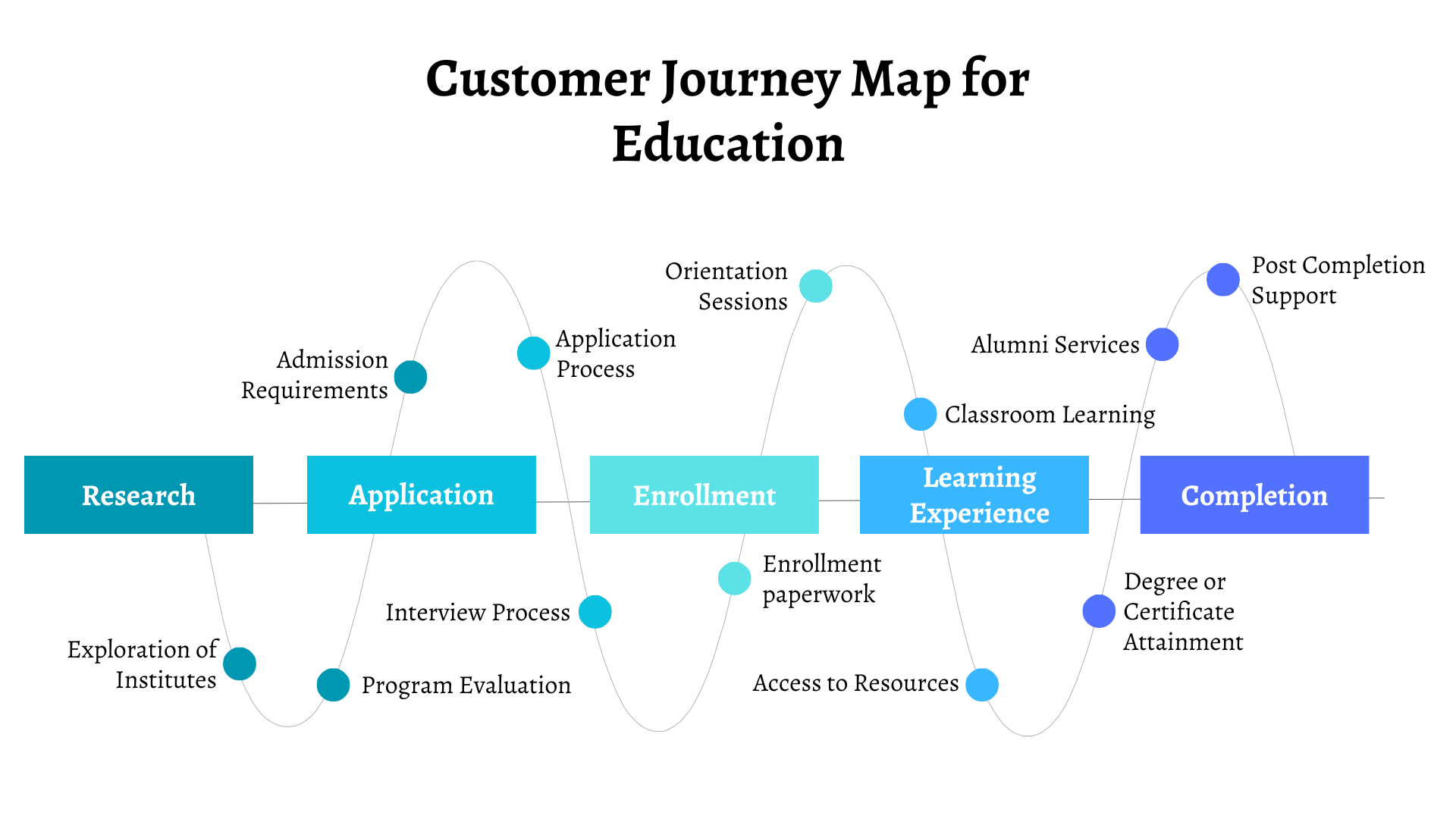
Customer Journey Map for Education
Education institutions aim to support students throughout their academic journey, from the application process to graduation and beyond.
Stage 1. Research
Prospective students research educational institutions, programs, and admission requirements.
- Exploration of Educational Institutions: Prospective students research different educational institutions, exploring their websites, brochures, rankings, and reviews to gather information about academic programs, faculty, campus facilities, and student life.
- Program Evaluation: Students evaluate academic programs offered by various institutions, considering factors such as curriculum structure, course offerings, accreditation, career prospects, and alumni success stories.
- Admission Requirements: Students review admission requirements, including academic qualifications, standardized test scores, letters of recommendation, essays, and application deadlines, to determine eligibility for their desired programs.
Stage 2. Application
Submission of application materials, communication with admissions staff, and interview process.
- Submission of Application Materials: Students complete and submit application forms, along with required materials such as transcripts, test scores, essays, and recommendation letters, either online or through mail.
- Communication with Admissions Staff: Students communicate with admissions counselors or staff members to seek clarification on application procedures, requirements, deadlines, and any special circumstances or accommodations needed.
- Interview Process: Some institutions may require students to participate in interviews as part of the admission process, providing an opportunity for applicants to discuss their academic interests, career goals, and personal experiences.
Stage 3. Enrollment
Acceptance, enrollment paperwork, and orientation sessions.
- Acceptance Notification: Students receive notification of their admission status, including acceptance, rejection, or waitlisting, along with details regarding enrollment deadlines, tuition fees, financial aid, and scholarship opportunities.
- Enrollment Paperwork: Accepted students complete enrollment paperwork, including acceptance forms, financial aid applications, housing contracts, health insurance forms, and other administrative documents required for enrollment.
- Orientation Sessions: Institutions organize orientation sessions or events to welcome incoming students, providing information about campus resources, academic programs, student services, campus life, and extracurricular activities.
Stage 4. Learning Experience
Classroom instruction, interaction with instructors and peers, and access to resources.
- Classroom Instruction: Students attend classes and lectures, engage in discussions, participate in group projects, and complete assignments, quizzes, exams, and presentations as part of their academic coursework.
- Interaction with Instructors and Peers: Students interact with professors, instructors, teaching assistants, and fellow classmates, seeking guidance, feedback, support, and collaboration in their academic pursuits.
- Access to Resources: Students utilize campus resources such as libraries, laboratories, computer centers, tutoring services, academic advising, career counseling, and extracurricular clubs and organizations to enhance their learning experience and personal development.
Stage 5. Graduation/Completion
Degree or certificate attainment, alumni services, and post-graduation support.
- Degree or Certificate Attainment: Students fulfill academic requirements and successfully complete their coursework, earning degrees, diplomas, or certificates in their respective fields of study.
- Alumni Services: Graduates become alumni of the institution, gaining access to alumni networks, career services, mentorship programs, professional development opportunities, and exclusive events or benefits offered to alumni.
- Post-Education Support: Institutions provide ongoing support to alumni, including access to job postings, career counselling, continuing education programs, alumni reunions, networking events, and opportunities for community engagement and philanthropy.
Example: Coursera
Coursera, an online learning platform, utilizes customer journey mapping to enhance the learning experience for students enrolled in its courses. They analyze user interactions on their platform, from course discovery to completion, to identify areas for improvement.
Successful Strategy: Coursera's personalized course recommendations based on learners' interests and skill levels are a successful strategy. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, they deliver tailored learning paths that align with each student's goals, increasing engagement and course completion rates.
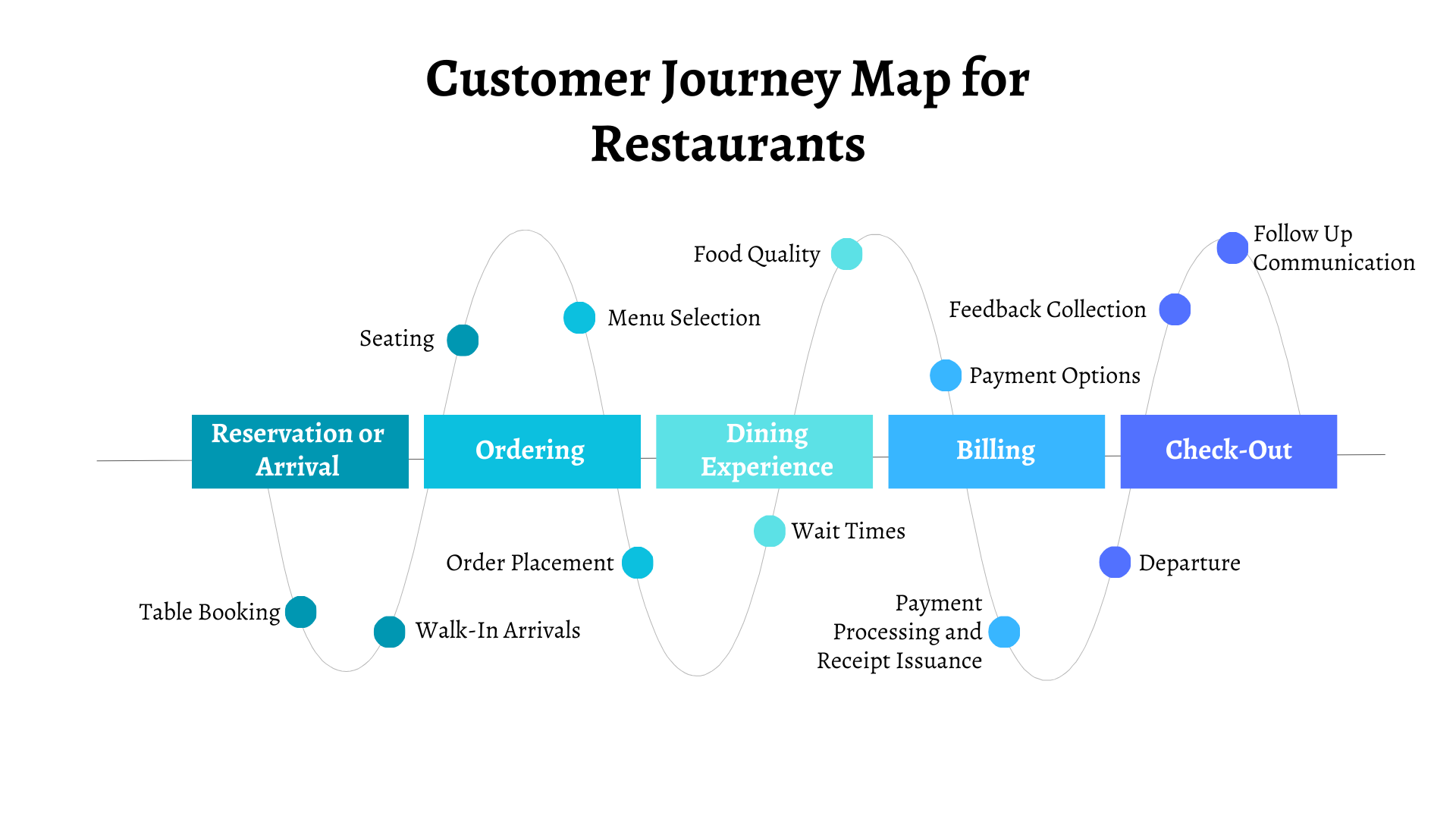
Customer Journey Map for Restaurants
Restaurants strive to provide exceptional dining experiences by optimizing touchpoints that begin with reservation and end with diners checking out of the restaurant.
Stage 1. Table Reservation/Arrival
Guests make reservations or walk in, are greeted by restaurant staff, and are seated at a table.
- Reservation Booking: Guests make reservations through phone calls, online booking platforms, or restaurant websites to secure a table for their desired date and time.
- Walk-in Arrivals: Guests arrive at the restaurant without prior reservations and are greeted by restaurant staff, who assess availability and accommodate them accordingly.
- Seating: Hosts or hostesses guide guests to their designated tables, ensuring a smooth and welcoming start to their dining experience.
Stage 2. Ordering
Menu selection, assistance with dietary restrictions, and placing orders with servers.
- Menu Selection: Guests review the menu offerings, including appetizers, entrees, beverages, and desserts, to make their dining selections based on personal preferences and dietary restrictions.
- Assistance with Dietary Restrictions: Guests may seek assistance from servers or restaurant staff to accommodate dietary restrictions or preferences, such as vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, or allergy-sensitive options.
- Placing Orders with Servers: Guests place their orders with servers or waitstaff, providing specific instructions or customization requests for their meals, beverages, and any additional services or accommodations needed.
Stage 3. Dining Experience
Food quality, presentation, wait times, and interactions with waiters and other staff.
- Food Quality: Guests enjoy the taste, freshness, and presentation of their meals, expecting high-quality ingredients, skilled culinary preparation, and appealing plating aesthetics.
- Service Interaction: Guests interact with servers and restaurant staff throughout their dining experience, receiving attentive and courteous service, assistance with menu choices, and prompt responses to inquiries or requests.
- Wait Times: Guests expect reasonable wait times for food preparation, table service, and overall dining experience, minimizing delays and ensuring a smooth flow of service from appetizers to dessert.
Stage 4. Billing
Payment processing, availability of payment options, receipt issuance.
- Payment Processing: Guests settle their bills through various payment methods, including cash, credit/debit cards, mobile payment apps, or gift certificates, processed securely by restaurant staff or automated payment systems.
- Availability of Payment Options: Restaurants offer flexible payment options to accommodate guest preferences, including split bills, contactless payments, and loyalty program rewards or discounts.
- Receipt Issuance: Guests receive itemized receipts detailing their orders, including menu items, prices, taxes, and any additional charges, ensuring transparency and accuracy in billing.
Stage 5. Check-out
Check-out of the restaurant, collection of feedback on the dining experience, follow-up communication, and incentives for return visits.
- Departure: Guests conclude their dining experience and prepare to leave the restaurant, thanking restaurant staff for their service and hospitality.
- Collection of Feedback: Restaurants may solicit feedback from guests regarding their dining experience, inviting them to share comments, suggestions, or compliments to improve service quality and customer satisfaction.
- Follow-up Communication: Restaurants may follow up with guests after their visit, expressing gratitude for their patronage and inviting them to return for future dining occasions, special events, promotions, or loyalty program benefits.
Example: Starbucks
Starbucks employs customer journey mapping to optimize the customer's experience across its global network of coffee shops. They focus on enhancing convenience, personalization, and brand loyalty through various customer touchpoints, including mobile ordering, loyalty programs, and in-store interactions.
Successful Strategy: Starbucks' mobile order and pay feature is a successful strategy. Customers can place orders and pay through the Starbucks mobile app, allowing for seamless pickup and customization of their favorite drinks, enhancing convenience and reducing wait times.
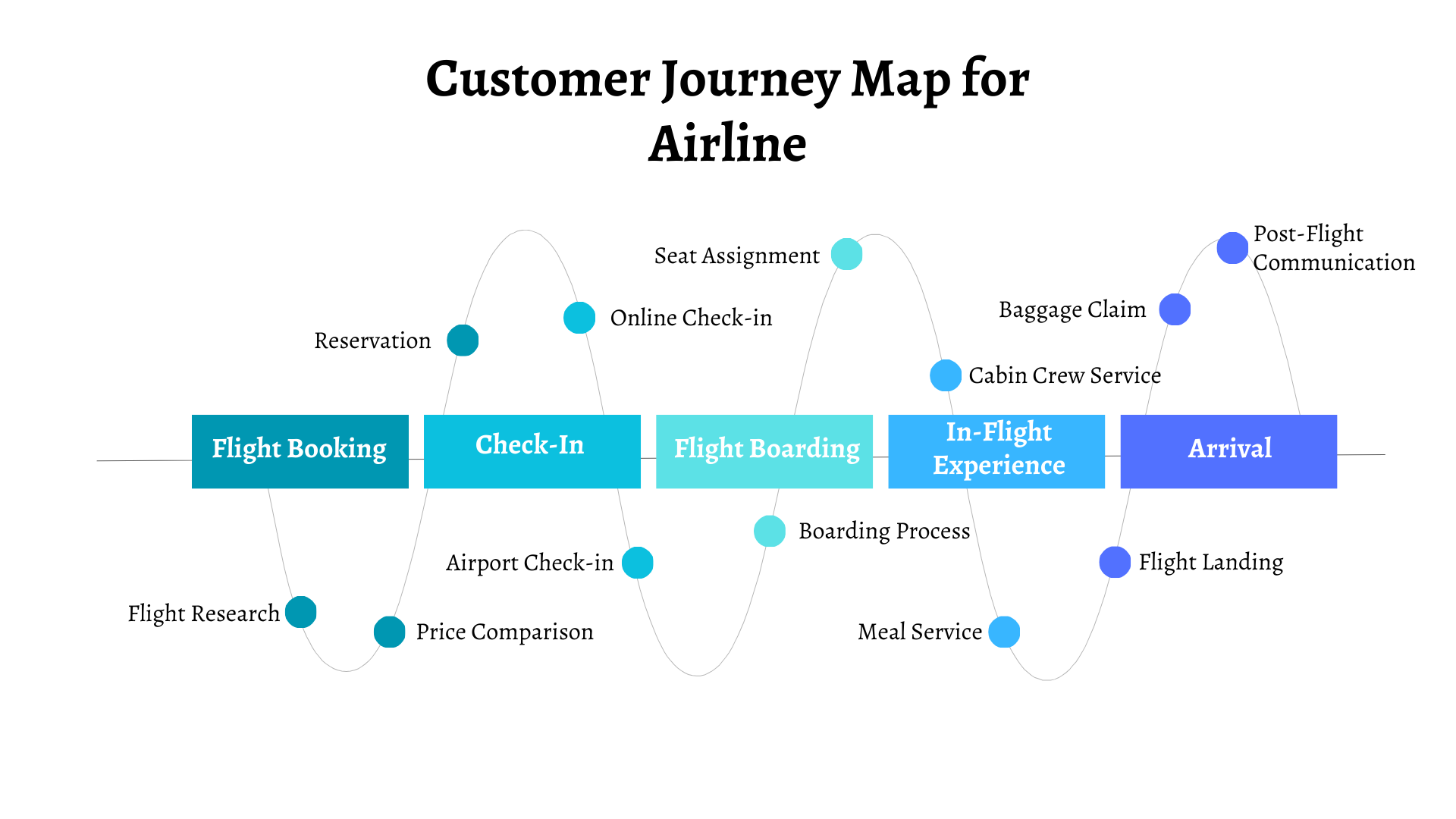
Customer Journey Map for Airline
Airlines focus on delivering seamless travel experiences by optimizing touchpoints that span from booking flights to post-flight communication.
Stage 1. Booking
Customers research flights, compare prices, and make reservations online or through a travel agent.
- Flight Research: Customers explore various flight options, destinations, dates, and prices through airline websites, online travel agencies (OTAs), or mobile apps, seeking the best deals and itineraries for their travel needs.
- Price Comparison: Customers compare fares, fees, and additional services offered by different airlines to make informed booking decisions based on factors such as affordability, convenience, and loyalty program benefits.
- Reservation: Customers finalize their flight bookings by selecting preferred options, entering passenger information, and making payment transactions securely online or through authorized booking channels.
Stage 2. Check-in
Online check-in or at the airport, issuance of boarding passes, and luggage drop-off.
- Online Check-in: Customers check-in for their flights conveniently through airline websites or mobile apps, selecting seats, updating passenger details, and receiving electronic boarding passes to streamline airport procedures.
- Airport Check-in: Customers complete check-in procedures at designated airport counters or self-service kiosks, where they receive physical boarding passes, drop off checked luggage, and seek assistance from airline staff as needed.
Stage 3. Boarding
Boarding process, seat assignment, and assistance for passengers with special needs.
- Boarding Process: Customers proceed through boarding gates according to designated boarding zones or seat assignments, presenting boarding passes and travel documents for verification by airline staff before entering the aircraft.
- Seat Assignment: Customers locate their assigned seats or request seat changes based on availability, preferences, or special requirements, ensuring comfortable seating arrangements for the duration of the flight.
- Special Assistance: Airlines provide personalized assistance and accommodations for passengers with special needs, including elderly passengers, unaccompanied minors, passengers with disabilities, or those requiring medical attention.
Stage 4. In-Flight Experience
Cabin crew service, in-flight entertainment, meal service, and comfort amenities.
- Cabin Crew Service: Customers receive attentive service and assistance from cabin crew members throughout the flight, including greetings, safety demonstrations, inflight meal/beverage service, and provision of amenities or comfort items.
- In-flight Entertainment: Customers access a variety of entertainment options, such as movies, TV shows, music, games, or reading materials, via personal seatback screens, overhead monitors, or personal electronic devices connected to onboard Wi-Fi or entertainment systems.
- Meal Service: Customers enjoy inflight dining experiences featuring a selection of meals, snacks, and beverages served by cabin crew members, accommodating dietary preferences or special meal requests as necessary.
Stage 5. Arrival
Flight leaving, baggage claim, and post-flight communication for feedback or future travel opportunities.
- Flight Landing: Customers disembark from the aircraft upon arrival at the destination airport, following instructions from cabin crew members and airport staff to exit the aircraft safely and efficiently.
- Baggage Claim: Customers retrieve checked luggage from designated baggage claim areas, identifying their belongings and proceeding through customs and immigration procedures as required.
- Post-flight Communication: Airlines may engage with customers after their flight to solicit feedback, offer assistance, or provide information on future travel opportunities, loyalty program benefits, or promotional offers.
Example: Southwest Airlines
Southwest Airlines utilizes customer journey mapping to deliver exceptional travel experiences for its passengers. They analyze the end-to-end travel journey, from booking flights to post-flight communication, to identify opportunities for improvement and innovation.
Successful Strategy: Southwest's customer-centric approach to flight scheduling and flexible booking policies is a successful strategy. By offering no change fees and generous refund policies, they provide customers with peace of mind and flexibility, fostering loyalty and trust in the airline brand.
Understanding the Customer Lifecycle
While customer journey mapping provides insights into the various touchpoints and experiences that customers go through, it's essential to also consider the broader context of the customer lifecycle. The customer lifecycle refers to the stages that individuals pass through as they interact with a business, from initial awareness to becoming loyal advocates. Understanding the customer lifecycle allows businesses to tailor their strategies and initiatives to meet the evolving needs and expectations of customers at each stage.
Stages of the Customer Lifecycle
-
Awareness: At this stage, customers become aware of a business or its products/services. They may come across the brand through advertising, social media, or word-of-mouth recommendations.
-
Consideration: Customers actively research and evaluate different options before making a purchase decision. They compare features, prices, and reviews to determine the best solution that meets their needs.
-
Purchase: Once customers have made a decision, they proceed to make a purchase. This could involve completing an online transaction, visiting a physical store, or engaging with a sales representative.
-
Retention: After making a purchase, businesses aim to retain customers and encourage repeat purchases. This involves providing ongoing support, personalized communication, and loyalty rewards to foster a long-term relationship.
-
Advocacy: Loyal customers who are satisfied with their experiences may become advocates for the brand. They recommend the business to others, leave positive reviews, and engage with the brand's community, contributing to its growth and reputation.
Relation between Customer Journey Mapping and Customer Lifecycle
The customer lifecycle and customer journey mapping are interconnected, with each stage of the lifecycle influencing the customer's journey. Customer journey mapping helps businesses identify touchpoints and interactions that occur within each stage of the lifecycle, allowing them to optimize the customer experience and drive desired outcomes.
For instance, in the retail industry, a customer may first become aware of a clothing brand through social media advertising while browsing formal cocktail attire (Awareness stage). They then research different products and read reviews on the brand's website (Consideration stage) before making a purchase online (Purchase stage). After receiving their order, the brand sends personalized recommendations and offers to encourage future purchases (Retention stage). Satisfied with their experience, the customer shares their positive feedback on social media and recommends the brand to friends and family (Advocacy stage).
By understanding the customer lifecycle and integrating it with customer journey mapping, businesses can create cohesive strategies that effectively engage customers throughout their entire journey, from initial awareness to becoming loyal advocates. This holistic approach contributes to building strong customer relationships and driving sustainable growth.
Conclusion
Customer Journey Mapping is crucial to understand and optimize customer experience at various touchpoints and customer interactions with the business. Collecting customer feedback at every touchpoint or interaction can help you identify the pain points of your customers and take appropriate action to resolve customer issues and avoid them in future. This helps you to deliver better customer experiences at all touchpoints of the customer journey.
An effective customer feedback software like Zonka Feedback can help you gather customer feedback at all touchpoints of the customer journey across various channels. With Zonka Feedback, you can easily create surveys, share them at various touchpoints through relevant channels, collect and take action on feedback, and close the feedback loop to improve customer experience and satisfaction.
It also offers a free trial. Try Zonka Feedback for free for 14 days and harness the power of customer journey mapping and customer feedback to deliver amazing experiences for your customers and ultimately grow your business.











